Make a Windows program by stuffing bytes into a buffer and writing it to disk: no compiler, no assembler, no linker, no nothing! It was the obvious conclusion of my recent efforts to gain more control over what goes into my executables, and this time I could set every bit exactly as I wanted it. Yes, I am still a control freak.
I began with a simple C program called ExeBuilder to construct the buffer and write it to disk in a file named handmade.exe. ExeBuilder looks like this:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include <Windows.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
HANDLE hFile = CreateFile("handmade.exe", GENERIC_WRITE, 0, NULL, CREATE_ALWAYS,
FILE_ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, NULL);
BYTE* buf = (BYTE*) HeapAlloc(GetProcessHeap(), HEAP_ZERO_MEMORY, 1024);
DWORD exeSize = BuildExe(buf);
DWORD numberOfBytesWritten;
WriteFile(hFile, buf, exeSize, &numberOfBytesWritten, NULL);
HeapFree(GetProcessHeap(), 0, buf);
CloseHandle(hFile);
printf("wrote handmade.exe\n");
return 0;
}
All of the interesting work happens in BuildExe(). This function manually constructs a valid Windows PE header, filling the required header fields and leaving the optional ones zeroed, then creates a single .text section and fills it with a few bytes of program code. The program in this case doesn’t do much – it just returns the number 44.
Sorting out the PE header details and determining which fields were actually required was a chore. All my testing was performed under Windows 7 64-bit edition. If you try these examples on your PC, it appears that earlier versions of Windows were more permissive with PE headers, while Windows 8 and 10 may be more strict about empty PE fields.
Here’s my first implementation of BuildExe(), which makes a nice standard executable with a single .text section containing 4 bytes of code.
inline void setbyte(BYTE* pBuf, DWORD off, BYTE val) { pBuf[off] = val; }
inline void setword(BYTE* pBuf, DWORD off, WORD val) { *(WORD*)(&pBuf[off]) = val; }
inline void setdword(BYTE* pBuf, DWORD off, DWORD val) { *(DWORD*)(&pBuf[off]) = val; }
inline void setstring(BYTE* pBuf, DWORD off, char* val) { lstrcpy((char*)&pBuf[off], val); }
DWORD BuildExe(BYTE* exe)
{
// 1. DOS HEADER, 64 bytes
setstring(exe, 0, "MZ"); // DOS header signature is 'MZ'
setdword(exe, 60, 64); // DOS e_lfanew field gives the file offset to the PE header
// 2. PE HEADER, at offset DOS.e_lfanew, 24 bytes
setstring(exe, 64, "PE"); // PE header signature is 'PE\0\0'
setword(exe, 68, 0x14C); // PE.Machine = IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_I386
setword(exe, 70, 1); // PE.NumberOfSections = 1
setword(exe, 84, 208); // PE.SizeOfOptionalHeader = offset between the optional header and the section table
setword(exe, 86, 0x103); // PE.Characteristics = IMAGE_FILE_32BIT_MACHINE | IMAGE_FILE_EXECUTABLE_IMAGE | IMAGE_FILE_RELOCS_STRIPPED
// 3. OPTIONAL HEADER, follows PE header, 96 bytes
setword(exe, 88, 0x10B); // Optional header signature is 10B
setdword(exe, 104, 4096); // Opt.AddressOfEntryPoint = RVA where code execution should begin
setdword(exe, 116, 0x400000); // Opt.ImageBase = base address at which to load the program, 0x400000 is standard
setdword(exe, 120, 4096); // Opt.SectionAlignment = alignment of section in memory at run-time, 4096 is standard
setdword(exe, 124, 512); // Opt.FileAlignment = alignment of sections in file, 512 is standard
setword(exe, 136, 4); // Opt.MajorSubsystemVersion = minimum OS version required to run this program
setdword(exe, 144, 4096*2); // Opt.SizeOfImage = total run-time memory size of all sections and headers
setdword(exe, 148, 512); // Opt.SizeOfHeaders = total file size of header info before the first section
setword(exe, 156, 3); // Opt.Subsystem = IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_CUI, command-line program
setdword(exe, 180, 14); // Opt.NumberOfRvaAndSizes = number of data directories following
// 4. DATA DIRECTORIES, follows optional header, 8 bytes per directory
// offset and size for each directory is zero
// 5. SECTION TABLE, follows data directories, 40 bytes
setstring(exe, 296, ".text"); // name of 1st section
setdword(exe, 304, 4); // sectHdr.VirtualSize = size of the section in memory at run-time
setdword(exe, 308, 4096); // sectHdr.VirtualAddress = RVA for the section
setdword(exe, 312, 4); // sectHdr.SizeOfRawData = size of the section data in the file
setdword(exe, 316, 512); // sectHdr.PointerToRawData = file offset of this section's data
setdword(exe, 332, 0x60000020); // sectHdr.Characteristics = IMAGE_SCN_MEM_READ | IMAGE_SCN_MEM_EXECUTE | IMAGE_SCN_CNT_CODE
// 6. .TEXT SECTION, at sectHdr.PointerToRawData (aligned to Opt.FileAlignment)
setbyte(exe, 512, 0x6A); // PUSH
setbyte(exe, 513, 0x2C); // value to push
setbyte(exe, 514, 0x58); // POP EAX
setbyte(exe, 515, 0xC3); // RETN
return 516; // size of exe
}
The resulting file is 516 bytes. Check to make sure it works:
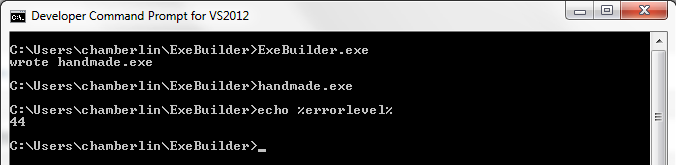
The executable is built from six data structures, which are numbered in the code’s comments. The cross-references in these structures are sometimes specified as offsets within the file, and sometimes as relative virtual addresses or RVAs. File offsets reflect the executable as it exists on disk, while RVAs reflect how it’s loaded in memory at run-time. An RVA is a run-time offset from the executable’s base address in memory. Getting these two confused will lead to problems!
DOS Header – The only fields that must be filled are the ‘MZ’ signature at the beginning and the e_lfanew parameter at the end (unless you’re actually writing a DOS program). e_lfanew gives the offset to the PE header, which in this case follows immediately after.
PE Header – The true PE header doesn’t contain much, because all the good stuff is in the optional header. The PE header specifies 1 section (the single .text section with the code to return 44), and 208 bytes combined size for the next two sections.
Optional Header – The optional header is only optional if you don’t care whether the program works. Some noteworthy values:
- SectionAlignment – Each section of the executable (.text, .data, etc) must be alignment to this boundary in memory at run-time. The standard is 4096 or 4K, the size of a single page of virtual memory.
- AddressOfEntryPoint – Program execution will begin at this memory offset from the base address. Because the section alignment is 4096, the program’s single .text section will be loaded at offset 4096, and execution should begin at the first byte of that section.
- FileAlignment – Similar to section alignment, but for the file on disk instead of the program in memory. The standard is 512 bytes, the size of a single disk sector.
- SizeOfHeaders – This isn’t really the combined size of all the headers, but rather the file offset to the first section’s data. Normally that’s the same as the combined size of all headers plus any necessary padding.
Data Directories – A typical executable would store offsets and sizes for its data directories here, the number of which is given in the optional header. Data directories are used to specify the program’s imports and exports, references to debug symbols, and other useful things. Manually constructing an import data directory is a bit complicated, so I didn’t do it. That’s why the program just returns 44 instead of doing something more interesting that would have required Win32 DLL imports. Handmade.exe does not have any data directories at all.
If you’re wondering why there are 14 data directories each with zero offset and size, instead of just specifying zero data directories, that’s a small mystery. According to tutorials I read, some parts of the OS will attempt to find info in data directories even if the number of data directories is zero. So the only safe way to have an empty data directory is to have a full table of offsets and sizes, all set to zero. However, I found other examples that did specify zero data directories and that reportedly worked fine. I didn’t look into the question any further, since it turned out not to matter anyway.
Section Table – For each section, there’s an entry here in the section table. Handmade.exe only has a single .text section, so there’s just one table entry. It gives the section size as 4 bytes, which is all that’s needed for the “return 44″ code. The section will be loaded in memory at RVA 4096, which is also the program’s entry point.
Section Data – Finally comes the actual data of the .text section, which is x86 machine code. This is the meat of the program. The section data must be aligned to 512 bytes, so there’s some padding between the section table and start of the section data.
Here’s what dumpbin says about this handmade executable. Many of the fields are zero or have bogus values, but it doesn’t seem to matter:
Microsoft (R) COFF/PE Dumper Version 11.00.50727.1
Copyright (C) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
Dump of file handmade.exe
PE signature found
File Type: EXECUTABLE IMAGE
FILE HEADER VALUES
14C machine (x86)
1 number of sections
0 time date stamp Wed Dec 31 16:00:00 1969
0 file pointer to symbol table
0 number of symbols
D0 size of optional header
103 characteristics
Relocations stripped
Executable
32 bit word machine
OPTIONAL HEADER VALUES
10B magic # (PE32)
0.00 linker version
0 size of code
0 size of initialized data
0 size of uninitialized data
1000 entry point (00401000)
0 base of code
0 base of data
400000 image base (00400000 to 00401FFF)
1000 section alignment
200 file alignment
0.00 operating system version
0.00 image version
4.00 subsystem version
0 Win32 version
2000 size of image
200 size of headers
0 checksum
3 subsystem (Windows CUI)
0 DLL characteristics
0 size of stack reserve
0 size of stack commit
0 size of heap reserve
0 size of heap commit
0 loader flags
E number of directories
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Export Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Import Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Resource Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Exception Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Certificates Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Base Relocation Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Debug Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Architecture Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Global Pointer Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Thread Storage Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Load Configuration Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Bound Import Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Import Address Table Directory
0 [ 0] RVA [size] of Delay Import Directory
SECTION HEADER #1
.text name
4 virtual size
1000 virtual address (00401000 to 00401003)
4 size of raw data
200 file pointer to raw data (00000200 to 00000203)
0 file pointer to relocation table
0 file pointer to line numbers
0 number of relocations
0 number of line numbers
60000020 flags
Code
Execute Read
Summary
1000 .text
Sometimes a picture is worth 1000 words, so I also made a color-coded hex dump of the executable file:
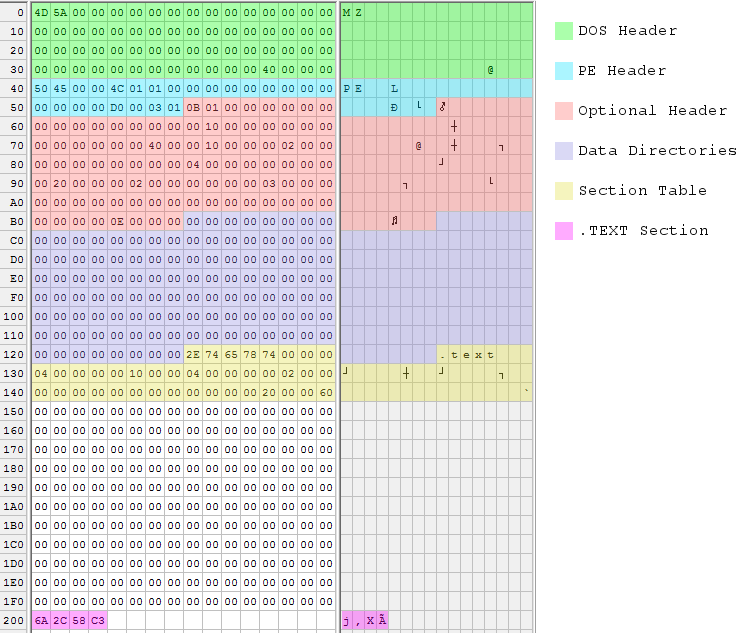
Shrinking It
After doing all this, of course my first thought was to try making it smaller. There’s a lot of empty padding between the section table and the section data, due to the 512 byte alignment of sections in the file. There must be some way to shrink or eliminate that padding, right? I tried reducing Opt.FileAlignment to 4, moving the .TEXT section data down to 336, and adjusting sectHdr.PointerToRawData accordingly. All I got for my effort was an error complaining “handmade.exe is not a valid Win32 application.” I’m unsure why it didn’t work. Maybe the OS doesn’t like sections that aren’t 512 byte aligned in the file, no matter what the PE header says.
Then I thought maybe I could reuse the header as the section data. By changing sectHdr.PointerToRawData to 0, I could make the Windows loader use a copy of the executable header as the .TEXT section data. 0 is 512 byte aligned, so there wouldn’t be any alignment problems. It seemed strange, since an executable header is not x86 code, but by stuffing the 4 bytes of code into an unused area of the header and adjusting Opt.AddressOfEntryPoint, I could theoretically patch everything up. Lo and behold, it worked! The new executable was only 340 bytes.
With the 4 bytes of code now stored inside the header, I wondered if I really needed a section at all. The Windows loader will load the header into memory along with all the sections, so maybe I could just eliminate the .TEXT section completely, and rely on the entry point address to point the way to the code stored in the header?
This worked too, but not without a lot of futzing around. After setting PE.NumberOfSections to 0, PE.SizeOfOptionalHeader and Opt.SizeOfHeaders both had to be set to zero. They’re both essentially offsets to section structures, and with no sections, apparently a 0 offset is required. Opt.SectionAlignment also had to be reduced to 2048, and I honestly have no idea why. With those changes, the modified program worked.
With the elimination of the section table, this should have been enough to shrink the executable to 300 bytes, but I found that anything smaller than 328 bytes wouldn’t work. It appeared that the OS assumes a minimum size for the optional header or the data directories, regardless of the sizes specified in the header. So 28 bytes of padding are required at the end of handmade.exe. The 328 byte version of BuildExe() is shown here, with the changes from the previous version highlighted:
DWORD BuildExe(BYTE* exe)
{
// 1. DOS HEADER, 64 bytes
setstring(exe, 0, "MZ"); // DOS header signature is 'MZ'
setdword(exe, 60, 64); // DOS e_lfanew field gives the file offset to the PE header
// 2. PE HEADER, at offset DOS.e_lfanew, 24 bytes
setstring(exe, 64, "PE"); // PE header signature is 'PE\0\0'
setword(exe, 68, 0x14C); // PE.Machine = IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_I386
setword(exe, 70, 0); // PE.NumberOfSections = 1
setword(exe, 84, 0); // PE.SizeOfOptionalHeader = offset between the optional header and the section table
setword(exe, 86, 0x103); // PE.Characteristics = IMAGE_FILE_32BIT_MACHINE | IMAGE_FILE_EXECUTABLE_IMAGE | IMAGE_FILE_RELOCS_STRIPPED
// 3. OPTIONAL HEADER, follows PE header, 96 bytes
setword(exe, 88, 0x10B); // Optional header signature is 10B
setdword(exe, 104, 296); // Opt.AddressOfEntryPoint = RVA where code execution should begin
setdword(exe, 116, 0x400000); // Opt.ImageBase = base address at which to load the program, 0x400000 is standard
setdword(exe, 120, 2048); // Opt.SectionAlignment = alignment of section in memory at run-time, 4096 is standard
setdword(exe, 124, 512); // Opt.FileAlignment = alignment of sections in file, 512 is standard
setword(exe, 136, 4); // Opt.MajorSubsystemVersion = minimum OS version required to run this program
setdword(exe, 144, 4096*2); // Opt.SizeOfImage = total run-time memory size of all sections and headers
setdword(exe, 148, 0); // Opt.SizeOfHeaders = total file size of header info before the first section
setword(exe, 156, 3); // Opt.Subsystem = IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_CUI, command-line program
setdword(exe, 180, 14); // Opt.NumberOfRvaAndSizes = number of data directories following
// 4. DATA DIRECTORIES, follows optional header, 8 bytes per directory
// offset and size for each directory is zero
// 5. SECTION TABLE, follows data directories, 40 bytes
// no section table
// 6. .TEXT SECTION, at sectHdr.PointerToRawData (aligned to Opt.FileAlignment)
setbyte(exe, 296, 0x6A); // PUSH
setbyte(exe, 297, 0x2C); // value to push
setbyte(exe, 298, 0x58); // POP EAX
setbyte(exe, 299, 0xC3); // RETN
return 328; // size of exe
}
Here’s another pretty picture, showing the 328 byte executable file:
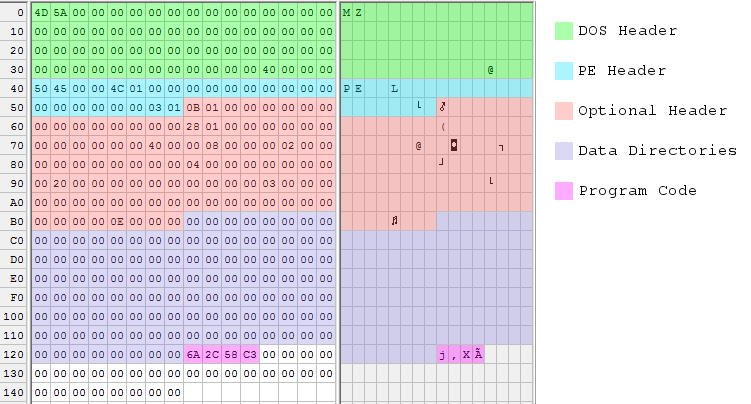
Maximum Shrinking
328 bytes was pretty good, but of course I wanted to do better. A popular technique seen in other “small PE” examples is to move down the PE header and everything that follows it, so that it overlaps the DOS header. This is possible because most of the DOS header is just wasted space, as far as a Windows executable is concerned.
The PE header can be moved down as low as offset 4 within the file. It must be 4-byte aligned, and it can’t be at offset 0 because then it would overwrite the required ‘MZ’ signature at the start of the file. Doing this is simple: just move everything but the DOS header down by 60 bytes.
The only complication with overlapping the DOS and PE headers this way is with the DWORD at file offset 60. This value is the e_lfanew parameter that gives the file offset to the PE header, so it now must be 4. But due to the overlapping, it’s also the Opt.SectionAlignment parameter that specifies the alignment between sections in memory at run-time. Hopefully Windows is OK with a 4-byte section alignment! It turns out that it’s fine, but only if Opt.FileAlignment is also 4. I’m not sure why.
These changes should have been enough to shrink the file to 240 bytes, but once again the OS seems to require 28 bytes of padding at the end of the file. Here’s the updated 268 byte version of BuildExe():
DWORD BuildExe(BYTE* exe)
{
// 1. DOS HEADER, 64 bytes
setstring(exe, 0, "MZ"); // DOS header signature is 'MZ'
// don't set DOS.e_lfanew, it's part of the overlapped PE header
// 2. PE HEADER, at offset DOS.e_lfanew, 24 bytes
setstring(exe, 64-60, "PE"); // PE header signature is 'PE\0\0'
setword(exe, 68-60, 0x14C); // PE.Machine = IMAGE_FILE_MACHINE_I386
setword(exe, 70-60, 0); // PE.NumberOfSections = 1
setword(exe, 84-60, 0); // PE.SizeOfOptionalHeader = offset between the optional header and the section table
setword(exe, 86-60, 0x103); // PE.Characteristics = IMAGE_FILE_32BIT_MACHINE | IMAGE_FILE_EXECUTABLE_IMAGE | IMAGE_FILE_RELOCS_STRIPPED
// 3. OPTIONAL HEADER, follows PE header, 96 bytes
setword(exe, 88-60, 0x10B); // Optional header signature is 10B
setdword(exe, 104-60, 296-60); // Opt.AddressOfEntryPoint = RVA where code execution should begin
setdword(exe, 116-60, 0x400000); // Opt.ImageBase = base address at which to load the program, 0x400000 is standard
setdword(exe, 120-60, 4); // Opt.SectionAlignment = alignment of section in memory at run-time, 4096 is standard
setdword(exe, 124-60, 4); // Opt.FileAlignment = alignment of sections in file, 512 is standard
setword(exe, 136-60, 4); // Opt.MajorSubsystemVersion = minimum OS version required to run this program
setdword(exe, 144-60, 4096*2); // Opt.SizeOfImage = total run-time memory size of all sections and headers
setdword(exe, 148-60, 0); // Opt.SizeOfHeaders = total file size of header info before the first section
setword(exe, 156-60, 3); // Opt.Subsystem = IMAGE_SUBSYSTEM_WINDOWS_CUI, command-line program
setdword(exe, 180-60, 14); // Opt.NumberOfRvaAndSizes = number of data directories following
// 4. DATA DIRECTORIES, follows optional header, 8 bytes per directory
// offset and size for each directory is zero
// 5. SECTION TABLE, follows data directories, 40 bytes
// no section table
// 6. .TEXT SECTION, at sectHdr.PointerToRawData (aligned to Opt.FileAlignment)
setbyte(exe, 296-60, 0x6A); // PUSH
setbyte(exe, 297-60, 0x2C); // value to push
setbyte(exe, 298-60, 0x58); // POP EAX
setbyte(exe, 299-60, 0xC3); // RETN
return 268; // size of exe
}
And another pretty picture, with some color blending going on where data structures overlap:
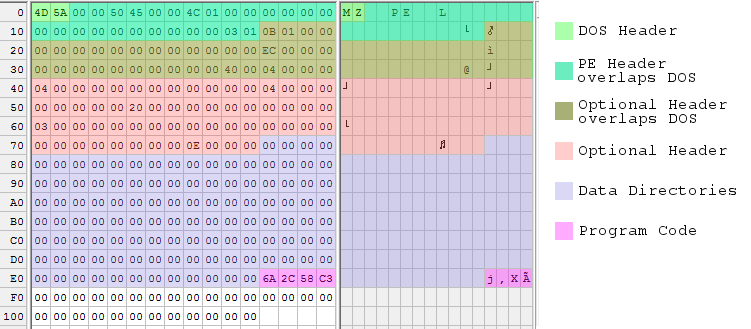
According to several sources, 268 bytes is the absolute minimum size for a working executable under Windows 7 64-bit edition. There are other tricks that would shrink the header even more, but then I’d just have to add more padding. I can go no further!